Table of Contents
What will become of our decentralized networks when quantum computers can break our most secure cryptographic defenses today? If quantum attacks eat away at digital security, then the security of blockchain systems has never been more crucial. Welcome to the Post Quantum Blockchain universe, an incoming paradigm shift strategy combining the blockchain’s resilience and the post-quantum cryptography’s next-generation security to protect the immortal digital universe.
In this article, we discuss the important part that quantum-resistant blockchain will have to play in protecting decentralized networks from the increasing menace of quantum computing.
Understanding Post-Quantum Blockchain
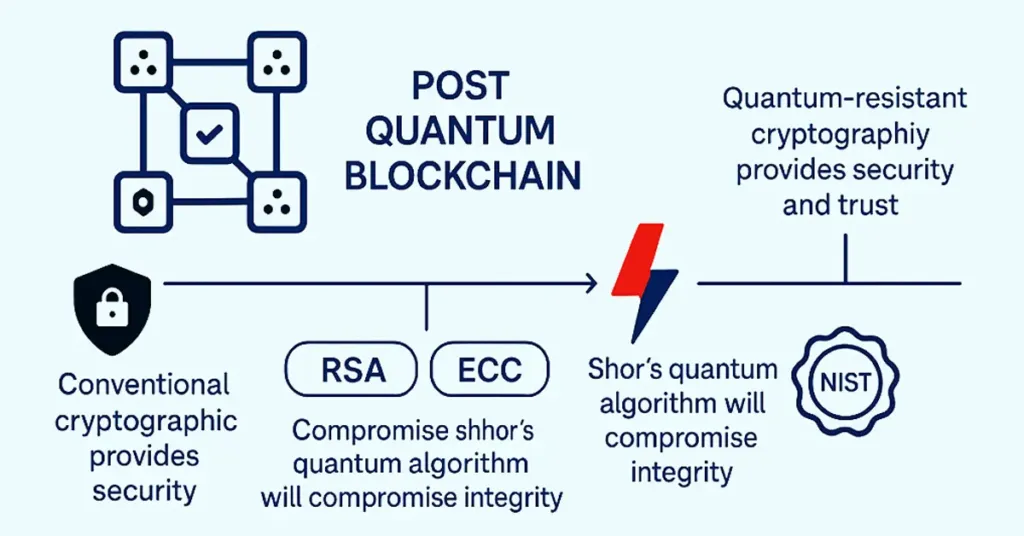
Post Quantum Blockchain is a blockchain network that is protected by highly advanced, quantum computer-immune cryptographically secured algorithms. RSA or ECC are conventional tools used for encryption, which would become sitting ducks against attacks from quantum algorithms like Shor’s, which will compromise their integrity. It poses a humongous risk to decentralized networks operating on such algorithms for data assurance, identity authentication, and secured transactions.
With the integration of quantum-resistant cryptography, these blockchain platforms can provide security and trust in a quantum computer-based future. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is attempting to develop ultimate encryption standards to be the new way of doing it, and hence quantum-secure blockchain deployment becomes an unavoidable evolution.
Why Traditional Blockchains Are Vulnerable

Although blockchain itself is generally considered secure and unalterable, it is not resistant to the increasing threat of quantum computing. Classical blockchains are highly dependent on classical cryptographic methods—namely, public-key cryptography—to protect digital identities, authenticate transactions, and establish consensus among distributed nodes. But with the accelerated advancement of quantum technology, these methods are in serious jeopardy. A sufficiently powerful quantum computer would be able to take advantage of loopholes in such cryptographic schemes to reverse-engineer private keys from public keys, allowing hackers to impersonate the real users. This can result in unauthorized transactions, loss of funds, or even bulk tampering with the blockchain ledger.
Furthermore, quantum computations like Shor’s algorithm can even break the digital signatures that are employed to secure transactions. If such signatures are compromised, they would no longer provide trust in the authenticity or source of a message. Quantum systems would also destabilize consensus systems, which are critical to all participants in a network adhering to a specified state of the blockchain. These findings point to how unprepared systems are at present for a quantum world.
In order to combat these future threats, cryptographers and developers are turning to Post Quantum Blockchain solutions that build on quantum-resistant protocols and algorithms. This next-generation solution can potentially restore trust and security in decentralized systems in the quantum era.
Core Principles Behind Post-Quantum Blockchain
To create a post-quantum blockchain that is resilient, some principles are used-
- Lattice-based cryptography: Lattice-based cryptography is a bedrock, since it is quantum proof. Its mathematical complexity is high and it’s computationally not possible even for quantum computers to reverse-engineer encrypted data, thus it’s a very secure way of safeguarding identity and key exchange.
- Hash-based signatures: Hash-based signatures constitute another central element. They provide secure short-term digital authentication to maintain messages and transactions tamper-evident. Hash-based signatures work with irrevocable one-way functions for a quantum system, as opposed to classical digital signatures.
- Code-based cryptography: Code-based cryptography is also used to ensure a good level of long-term message security. It uses codes that will resist such forms of decryption, whether classical or quantum.
- Zero-knowledge proofs: Finally, we have zero-knowledge proofs, which are incorporated to complete the system. Zero-knowledge proofs allow a party to verify possession of knowledge about a condition or value without sharing underlying information. This maintains confidentiality and guarantees immunity from quantum attacks, such that data confidentiality and trust are achieved in decentralized applications.
Advantages of Post-Quantum Blockchain
1. Future-Proof Security
Most readily apparent benefit of Post Quantum Blockchain is that it will resist quantum attacks. Avoiding future attacks ahead of time, the developers will not need to invest the exorbitant expense of redoing systems down the road.
2. More Privacy
New cryptographic building blocks employed by Post Quantum Blockchain can also enhance the protection of privacy through improved anonymization techniques.
3. Compliance with Regulations
As government agencies start to issue post-quantum compliance requirements, employing Quantum Blockchain protocols puts businesses ahead of the law.
4. Long-Term Data Integrity
In contrast to legacy systems that can grow obsolete in the quantum age, Post Quantum Blockchain solutions guarantee your data is immutable and trusted for decades to come.
Real-World Use Cases for Post-Quantum Blockchain
Some industries are starting to consider Post Quantum Blockchain-
- Finance: The banking industry, for example, is among the first to embrace. Encryption is a major source of security for online transactions, customer identity, and online balances for banks. With the danger of traditional cryptography from quantum computers, quantum-resistant blockchain guarantees long-term security for banking services, cryptocurrencies, and smart contracts.
- Healthcare: Healthcare, where the confidentiality and integrity of patient data are paramount, sees this technology providing tamper-evident storage and transport of sensitive information. Decentralization, and with it the use of quantum-safe encryption, makes for safe sharing of medical records between health providers and shields against leaks and unauthorized alteration.
- Supply Chain: The supply chain sector is also discovering the utility of this new solution. Through the utilization of quantum-resistant blockchain, businesses can create open, immutable records of product origin, transport, and handling. It assists in the prevention of fraud, lowers counterfeiting, and increases efficiency in international logistics.
- Government: Governments are exploring their use for secure administration of digital identity, citizenship authentication, and even voting. With election security and identity fraud issues on the rise, a tamper-proof, quantum-secure blockchain can provide more public trust and operational integrity to democratic and administrative systems.
The Rise of Post Quantum Secured Blockchain
Post quantum secured blockchain technology is a giant leap towards the security of decentralized platforms against the impending threat of quantum computers. Traditional blockchains, though secure against classical attacks, are becoming increasingly susceptible to quantum algorithms that support breaking standard encryption schemes employed.
Conversely, post quantum secured blockchain networks are inherently constructed with quantum resistance. Every single aspect—identity verification, transaction verification, smart contracts, and consensus algorithms—is supported by cryptographic algorithms particularly selected for their quantum decrypt resistance.
This method guarantees that important activities such as signing a contract, digital signing, and multi-party cooperation on data are secure, transparent, and tamper-evident even in the future when all have quantum processors. With a trend of industries going quantum-readiness, implementing such infrastructure is not an upgrade—it is a required building block.
METHODOLOGY: Ensuring AI Safety Through Post Quantum Blockchain
To truly safeguard AI’s influence on society, data integrity must be prioritized above all. As artificial intelligence systems become more intertwined with human decision-making, preventing malicious replication of identity and the misuse of personal data is crucial. One reliable approach is the integration of Post Quantum Blockchain with decentralized storage.
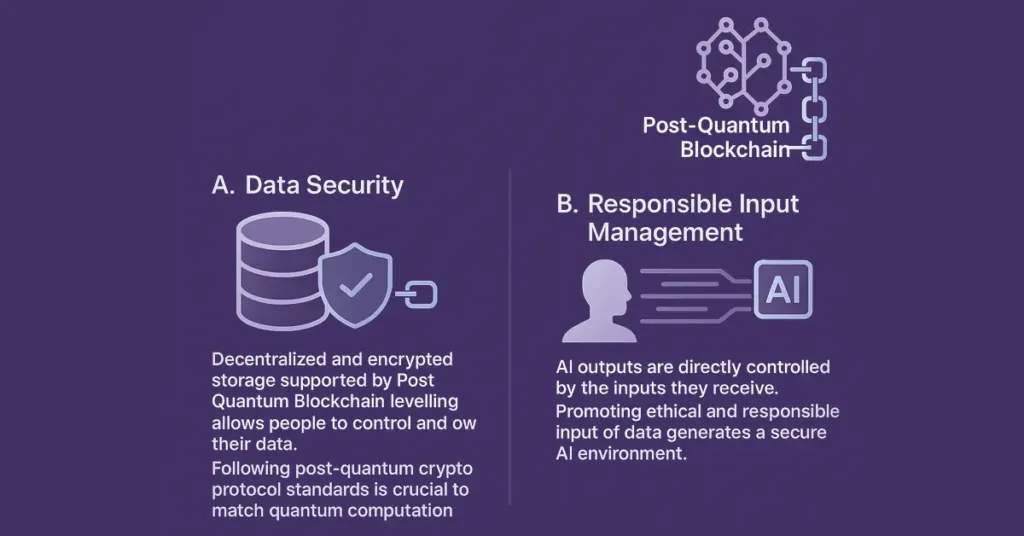
A. Data Security
Decentralized and encrypted storage supported by Post Quantum Blockchain levelling allows people to control and own their data. It is already under development in the form of such projects as NCOG for this juncture. In addition to that, following established post-quantum crypto protocol standards is most important to be able to match quantum computation’s powerful capabilities.
B. Responsible Input Management
AI outputs are directly controlled by the inputs that they receive. Promoting ethical and responsible input of data that is unbiased and not manipulated generates a secure AI environment. Through Post Quantum Blockchain, these standards generate secure and transparent systems that cannot be exploited or tampered with illegally.
Conclusion
The advent of quantum computing brings with it new threats—and new potential. This revolutionary time in the industry, Post Quantum Blockchain is a lighthouse through the darkness for the secure decentralized technology of tomorrow. Picking quantum-resistant cryptography today is not only about securing our data, but it is where we are securing the foundation of digital society for future generations. Artificial intelligence to medicine, finance to government, the transition to Post Quantum Blockchain isn’t just on the cards—it’s necessary.
References-
(Vishal Garg, Artificial Intelligence as a Second-Class Citizen: Safeguarding Humanity and Data Integrity, Volume 11 Issue 11, Page No: 512-514, ISSN: 2349-6002, 2025)
(Rob Clyde, Isaca, Alexander S. Gillis, post-quantum cryptography)
(Aykut Karakaya, Ahmet Ulu, A Review on Latest Developments in Post-Quantum Based Secure Blockchain Systems)
(Jesse Anglen, What is Quantum Resistant Blockchain? Types, Benefits, Challenges & Use Cases)
FAQs
What is Post Quantum Blockchain?
This is a quantum resistant blockchain platform that uses top rated cryptography that is resistant to threats from very strong quantum computers. Different from the other traditional cryptography methods, which can be penetrated during the era of quantum, this platform uses quantum-resistant algorithms to secure data, transactions, and digital identities. It offers a secure basis for decentralized platforms that need long-term security.
Why do we need Post Quantum Blockchain today?
Quantum computers are advancing at a fast pace, and our commonly used encryption systems like RSA and ECC are exposed to them. This new advancement compromises the security base of existing decentralized systems, exposing sensitive information and transactions to tampering and interception. To protect information in the long term and establish trust in digital economies, we need to deploy quantum-resistant technology today. Faster action allows for systems to develop safely and withstand future computational attacks by quantum computers.
In what way does blockchain challenge quantum computing?
Quantum computers utilize algorithms that can solve very complex math problems much more quickly than traditional computers, especially those on which traditional encryption techniques such as RSA and elliptic curve cryptography are based. If a hacker has access to a quantum computer, they can construct private keys from public keys, create counterfeit digital signatures, and reverse verified transactions. All of these circumvent the foundational assumptions of blockchain technology, like immutability and trust. Decentralized networks need to be protected, and encryption algorithms used must be strong enough to counter these new quantum attacks.
Is there any real-world example of Post Quantum Blockchain in use?
Indeed, some actual projects are investigating the application of quantum-resistant technology to protect decentralized systems. The NCOG Earth Chain, for instance, is committed to the protection of digital identity and secure data exchange through enhanced cryptographic techniques. Apart from that, governments worldwide, such as the United States, Germany, and Japan, are promoting research and pilot projects that employ quantum-safe methods for sensitive applications such as electronic voting, secure document authentication, and secret communication.
Is it possible to upgrade existing blockchains to Post Quantum Blockchain?
It is difficult but possible to upgrade existing blockchain systems to be quantum-proof. Research into hybrid crypto approaches that combine standard encryption with quantum-proof cryptography continues. Solutions strive to be backwards compatible with the current infrastructure and introduce more robust security features. Hard forks, sidechains, or Layer-2 solutions are being experimented upon to enable incremental upgrades.
Is Post Quantum Blockchain solely for use by finance?
No, post-quantum blockchain technology isn’t simply just for monetary utilization alone. It has vast usefulness in fields where data trading and secrecy come foremost into play. In medical scenarios, it safeguards patient documents as well as clandestine medicating details. Within educational forums, it may ensure educational diplomas and counter theft. As regards government utilization, it ensures ballot tampering security as well as public documentation. Likewise, in supply chains, it offers secure and transparent product tracking. Any industry that depends on verifiable, secure data can be helped by this technology.
How does Post Quantum Blockchain help in AI development?
Quantum-resistant blockchain technology supports AI development by the protection of the training and decision making data ensuring it stays in an integrity and confidential state. It can’t allow AI systems to be misled by false or tainted inputs through verifiable data storage, nor can its outputs be erroneous or unreliable. Ethical deployment of AI necessitates such a shield, which renders data integrity paramount in ensuring the avoidance of fatal biases or misleading conclusions.
Why is Post Quantum Blockchain future-proof?
Quantum-resistant blockchain technology is future-proof because it employs encryption techniques specifically engineered to be able to resist the advanced capabilities of quantum computers. In contrast to conventional cryptography, which would be vulnerable to quantum algorithms, these new cryptography standards provide long-lasting security and integrity of data. This resistance provides robust protection to key systems, protecting digital assets and information far into the future regardless of quantum computing advancements.
Is Post Quantum Blockchain open-source?
Yes, most of the work towards developing quantum-resistant blockchain technology is open-source. Openness offers visibility, and allows several developers to implement and improve quantum-resistant protocols that protect against security threats. Open source projects encourage collaboration that helps advance innovation and makes sure that the technology will mature to counteract the influence of quantum computing threats.
When will Post Quantum Blockchain go mainstream?
The implementation schedule for post-quantum resistant blockchain technology across the general spheres is heavily dependent on the development of post-quantum standards by such bodies as NIST and the development of post-quantum computers. After developing these standards by NIST, the developers will begin to integrate them into blockchain systems to make them ready to be quantum-proof. Based on the rate of quantum computing research and blockchain development, worldwide adoption and implementation of quantum-resistant protocols are expected to happen within the next 5–10 years, as the technology develops further and becomes more widely accepted.
